下面是学习caffe框架时候的笔记,大部分来自caffe 官方文档, 阅读caffe code时的注释在 这里
概述
Caffe is a deep learn framework
- Expression: models and optimizations are defined as plaintext schemas instead of code.
- Speed: for research and industry alike speed is crucial for state-of-the-art models and massive data.
- Modularity: new tasks and settings require flexibility and extension.
- Openness: scientific and applied progress call for common code, reference models, and reproducibility.
- Community: academic research, startup prototypes, and industrial applications all share strength by joint discussion and development in a BSD-2 project.
Components四大组件
Blobs
Caffe使用blob来存储和传递数据
Blob提供了储存和访问数据(eg.图像数据、 模型参数、用于优化的delta数据)的统一接口
Blob提供了CPU和GPU之间的同步机制
Memory on the host and device is allocated on demand (lazily) for efficient memory usage.
传统的Blob是四维NCH*W
SyncedMemory
在主机(CPU)和设备(GPU)之间管理内存分配和数据同步,封装二者之间的交互操作
1 | const Dtype* foo; |
protobuf
格式化数据? C++写的东西,Python能用,MATLAB也能用
目前广泛使用的格式化数据主要有两种,Binary(C++、Python)、HDF5(MATLAB)
文本格式的体积要比二进制格式体积大5倍左右,读取速度也要相应慢上几倍,还存在安全性问题。文本型数据很容易被逆向破解掉。
二进制虽然体积小,但是需要人工设计封装格式。这给序列化(编码),反序列(解码),带来麻烦
Protocol Buffer 是由 google 开发的神奇工具
有着非常不错的格式化数据的序列化/反序列速度
支持文本格式
在自动生成序列化格式的同时,也封装了部分变量的访问接口。
proto语言与C语言差别不是很大,结构体struct字段等效message
repeated标记之后,本质是数组,但实际实现可能是类似于STL容器,它提供了不少类似容器的操作
使用[packed=true]似乎可以优化速度,但对于float其实是无效的
所有数据结构变量,都需要一个唯一的id,id从1开始。id与proto内部编码系统有关系,1~20编码长度小,访问速度快。随着id值增加,后续变量访问速度会递减。
1 | message Datum{ |
Datum算是最基本的存储单元了,它其实表示的就是一张图像。
1 | message BlobShape{ |
Blob提供序列化容器,用于存储训练参数。
protobuf使用的demo protobuf-use-demo
Layers
Layer是caffe中模型的基础,也是caffe中一个计算的基本单元
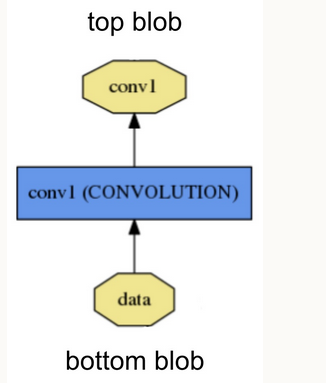
Setup: 在模型初始化时被调用,初始化layer和其connections.
Forward: 根据输入bottom blob计算得到输出送至top blob.
Backward: 根据top blob的gradient计算关于input的 gradient 并输出到bottom blob. 带有parameters的layer还会计算关于参数的gradient并store internally.
Nets
Net由layers连接,构成一个有向无环计算图(DAG).负责layers连接的正确性和forward&backward传递时的琐碎信息。
Net模型使用plaintext modeling language描述
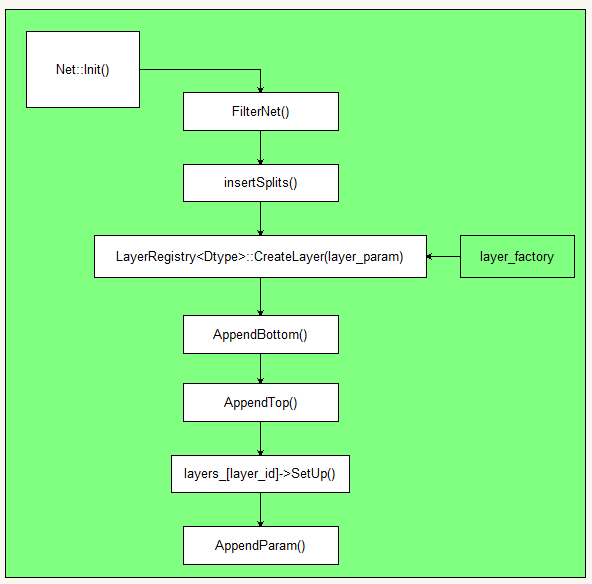
Net::init()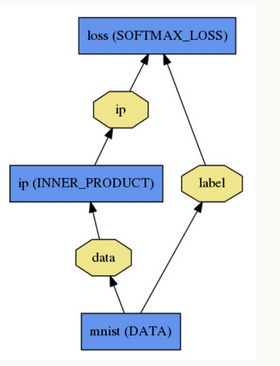
Log for Net::init()
Solvers
Solvers单独配置,负责协调网络的前向interence和后向gradients更新,以达到最小化loss的目的
Stochastic Gradient Descent (type: “SGD”),
AdaDelta (type: “AdaDelta”),
Adaptive Gradient (type: “AdaGrad”),
Adam (type: “Adam”),
Nesterov’s Accelerated Gradient (type: “Nesterov”) and
RMSprop (type: “RMSProp”)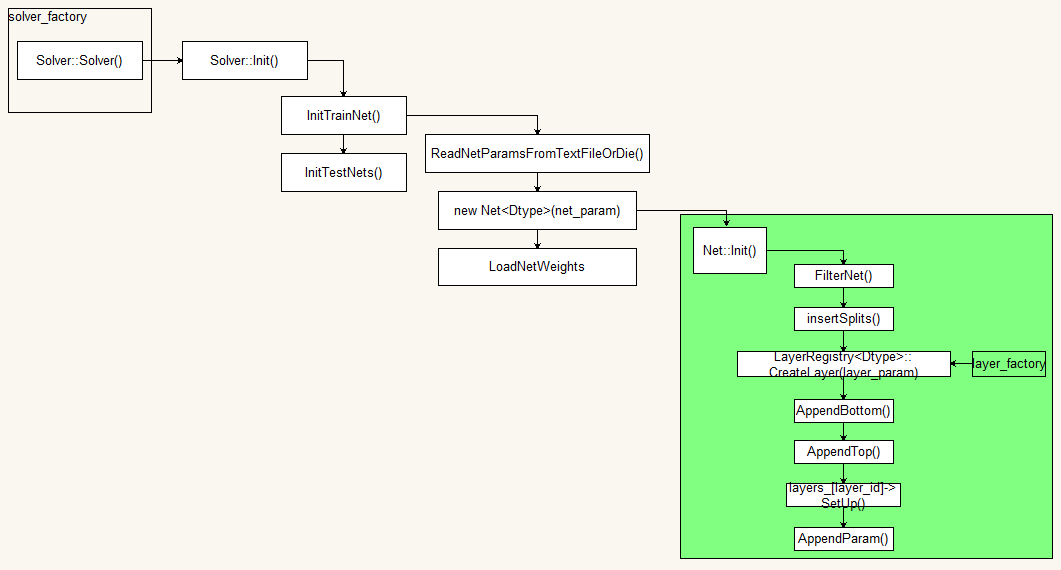
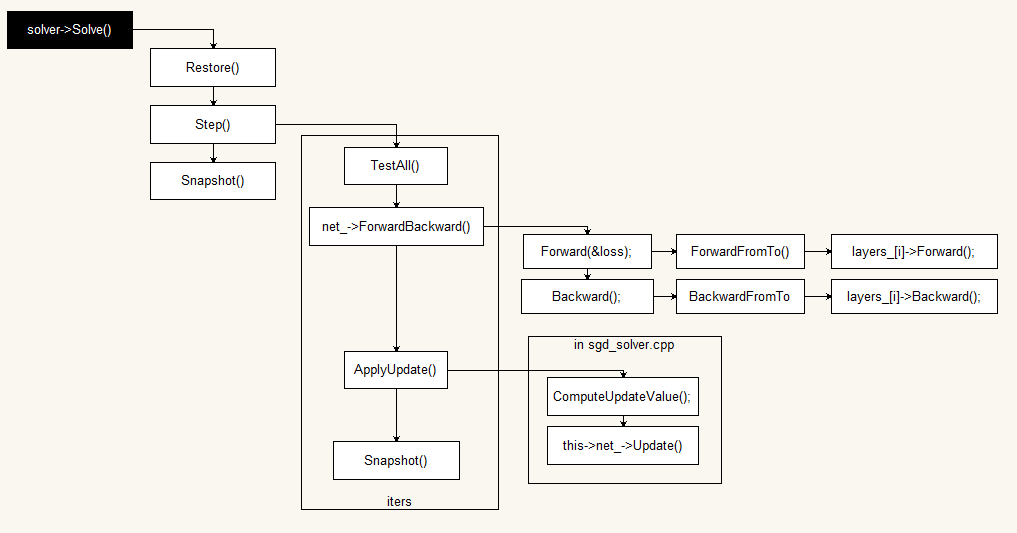
创建用于学习的训练网络和用于评估的测试网络并维护各种状态信息
迭代调用网络的 forward/backward 方法同时更新parameters.
周期性评估测试网络
优化过程中 snapshots the model and solver state
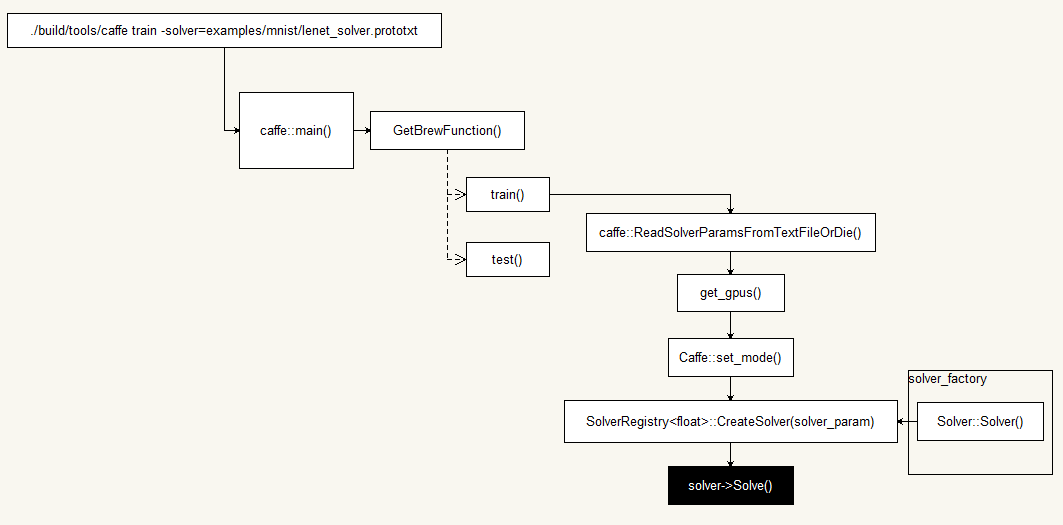
Workflow 代码流程
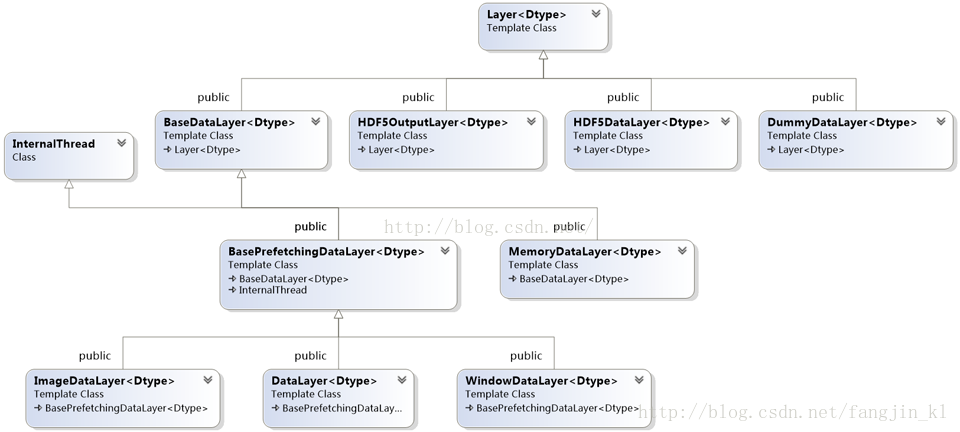
Layers 详细
data layers
数据 通过data layers进入caffe框架,data layers 处于整个网络的bottom层。
只有top blobs没有bottom blobs
普通的输入预处理(eg.mean subtraction, scaling,random cropping,and mirroring),某些layer可以通过指定 TransformationParameters完成,若layer没有TransformationParameters ,则可以借助 bias, scale, and crop layers
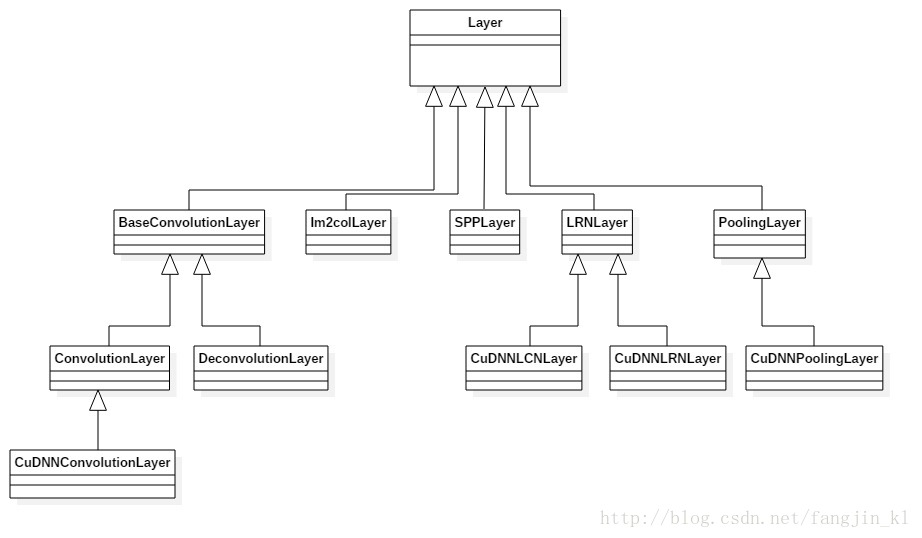
Vision-layers
通常以image作为输入,同时输出images。处理过程会考虑输入数据的空间信息(c,h,w),因此区别于其他以“big vector”作为输入的layers.
Convolution Layer: convolves the input image with a set of learnable filters, each producing one feature map in the output image.
Pooling Layer: max, average, or stochastic pooling.
Spatial Pyramid Pooling (SPP)
Crop: perform cropping transformation.
Deconvolution Layer: transposed convolution.
Im2Col: relic helper layer that is not used much anymore.
Custom layer
参考 这个
refs
官方文档
- http://caffe.berkeleyvision.org/tutorial/
- http://www.caffecn.cn/?/topic/
- https://blog.csdn.net/fangjin_kl/article/category/6654921/1
- http://www.cnblogs.com/denny402/category/759199.html
- https://dirtysalt.github.io/html/caffe.html
- https://www.cnblogs.com/empty16/p/4878164.html
- https://blog.csdn.net/edmond999/article/category/7202771
- https://blog.csdn.net/jiongnima/article/category/6436731/1
- https://blog.csdn.net/jiongnima/article/category/6436731
https://blog.csdn.net/wei1033701020/article/category/6636981
https://blog.csdn.net/u013108511/article/category/6795958
caffe alexnet
/root/caffe/examples/imagenet
在训练的时候,提到http://nbviewer.jupyter.org/github/BVLC/caffe/blob/master/examples/00-classification.ipynb
注意在调用download_model_binary.py的时候,需要将其改为python3.6解析,因为我是用的pip3.6 install的
protobuf及caffe.proto解析
https://blog.csdn.net/u012177034/article/details/53944901
1.《深度学习入门:基于Python的理论与实现.pdf》
山寨caffe,此人文章很深刻啊,对库,对vs,对c++
https://www.cnblogs.com/neopenx/category/786908.html